What Is Trichology
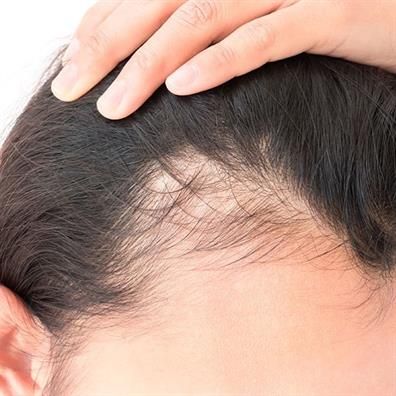
Trichology is the para-medical science of the hair, hair loss and associated scalp problems. It encompasses the study of the diseases of the human hair and scalp, as well as the assessment of the cause(s) and treatment of these disorders.
The word “trichology” comes from the Greek word, ‘Trikhos’, meaning ‘hair’, and was first conceived as a specialty branch of study in Britain in the late 19th century. It then became a specific para-medical discipline in 1902.
Today, trichology is perceived as the “bridge between cosmetology and dermatology.”